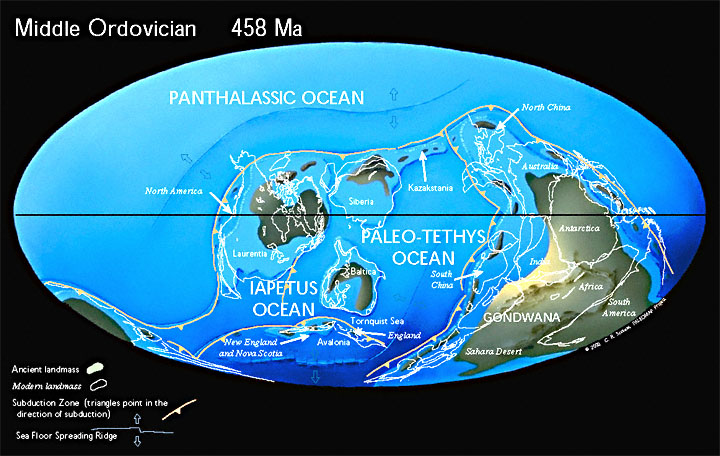
The Ordovician Period
The Ordovician Period lasted almost 45 million years, beginning 488.3 million years ago and ending 443.7 million years ago.* During this period, the area north of the tropics was almost entirely ocean, and most of the world’s land was collected into the southern supercontinent Gondwana. Throughout the Ordovician, Gondwana shifted towards the South Pole and much of it was submerged underwater.
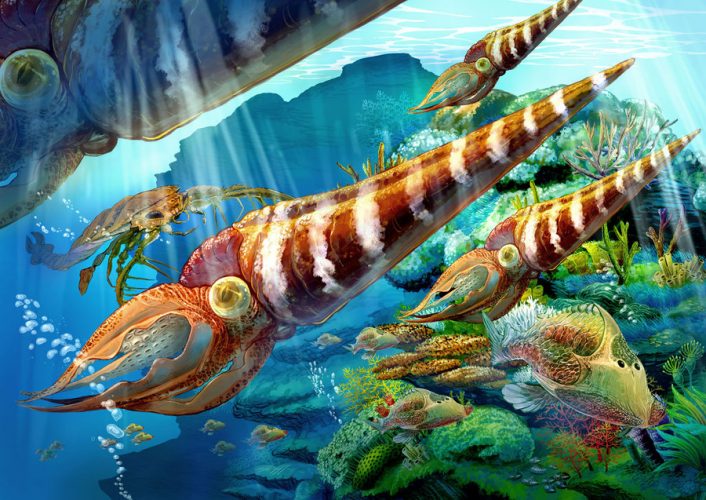
The Ordovician is best known for its diverse marine invertebrates, including graptolites, trilobites, brachiopods, and the conodonts (early vertebrates). A typical marine community consisted of these animals, plus red and green algae, primitive fish, cephalopods, corals, crinoids, and gastropods. More recently, tetrahedral spores that are similar to those of primitive land plants have been found, suggesting that plants invaded the land at this time.
From the Lower to Middle Ordovician, the Earth experienced a milder climate — the weather was warm and the atmosphere contained a lot of moisture. However, when Gondwana finally settled on the South Pole during the Upper Ordovician, massive glaciers formed, causing shallow seas to drain and sea levels to drop. This likely caused the mass extinctions that characterize the end of the Ordovician in which 60% of all marine invertebrate genera and 25% of all families went extinct.
Life
Ordovician strata are characterized by numerous and diverse trilobites and conodonts (phosphatic fossils with a tooth-like appearance) found in sequences of shale, limestone, dolostone, and sandstone. In addition, blastoids, bryozoans, corals, crinoids, as well as many kinds of brachiopods, snails, clams, and cephalopods appeared for the first time in the geologic record in tropical Ordovician environments. Remains of ostracoderms (jawless, armored fish) from Ordovician rocks comprise some of the oldest vertebrate fossils.
Despite the appearance of coral fossils during this time, reef ecosystems continued to be dominated by algae and sponges, and in some cases by bryozoans. However, there apparently were also periods of complete reef collapse due to global disturbances.
Source: www.ucmp.berkeley.edu










